|
TABLE OF CONTENTS
JD Introduction and Setup
1. Getting Started with JD 2. Using The Robot Program 3. Introduction to Robotics 4. JD Box Contents 5. Battery Care & Charging 6. Building JD Humanoid 7. Connecting to JD over WiFi 8. Using a USB Wi-Fi Dongle 9. Fine Tune JDs Servos 10. Care for JD 3D Printing for JD 1. 3D Print Files for JD Mobile App for JD 1. Using JD with Mobile App General CoursesSoftware 1. ARC for Windows PC 2. Example Projects 3. Controls 4. Getting Help with Controls 5. ControlCommand() 6. Virtual Desktops 7. RoboScratch 8. Blockly 9. EZ-Script Mobile Software 1. Create a Mobile App Linear Programming 1. Create a Scene Using RoboScratch (Big Hero Six) 2. Create a Scene using Blockly (Avengers) Logical Programming 1. Programming Concepts (Variables, If/Else, Logic) 2. Counting Up 3. Counting Down Camera Input 1. Introduction to the EZ-B Camera 2. Face Detection with RoboScratch 3. Face Detection with Blockly 4. Face Detection with EZ-Script 5. Color Tracking with Servos 6. Color Tracking with Movement 7. Detecting Multiple Colors 8. Line Following with Roli, AdventureBot and Shell-E 9. Vision - Object Training & Recognition 10. Glyphs to Control Robot Movement 11. Detecting Glyphs & Augmented Reality 12. QR Code Detect 13. Microsoft Cognitive Emotion 14. Microsoft Cognitive Vision Audio Input 1. Speech Recognition RGB Output 1. RGB Animations Positioning 1. Servo Control 2. Introduction to Servo Motors 3. Create a Robot Dance 4. Program Robot to Dab 5. Program Robot to Play Piano 6. MYO Gesture Armband Navigation and Movement 1. Movement Panels 2. Navigating using RoboScratch 3. Navigating using Blockly Creative Applications 1. Customize Your EZ-Robot 2. Control Robot From Twitter 3. Nest Thermostat EZ-B v4 Robot Brain 1. EZ-B v4 Robot Brain Overview 2. DIY Autonomous Robot Vehicle 3. EZ-B v4 and IoTiny Wi-Fi Modes 4. Change WiFi Name 5. Resetting Your EZ-B v4 or IoTiny 6. USB WiFi or Ethernet Adapter Robot Troubleshooting 1. Which Robot are You Using? |
Connecting to JD over WiFiIntroduction
In this lesson, we will explain how to connect to your JD robot using your PC. What You Will Need
Step 1 *Note: The ARC software is displayed in the instructions. EZ-Builder may have a slightly different looking interface. Load ARC and press the OPEN button under the FILE menu.
*Note: ARC is regularly updated. To access the latest features and capabilities, keep ARC updated. Within an education setting, you may want to only update ARC between semesters. Step 2 In ARC (formerly EZ-Builder), the Open File Dialog window will display. Press the EZ-Robot button at the top to open the Default Projects.
*Note: Projects are specific to each 'type of robot' and may be used with any robot of the same type, as long as they are assembled correctly and properly calibrated. Step 3 Locate the JD project and press the OPEN button.
Step 4 Your JD project is now loaded. If the software asks you to open Assembly Instructions, click 'Not Now'. It then may ask to Select a Servo Fine Tune profile. Click 'Skip'.
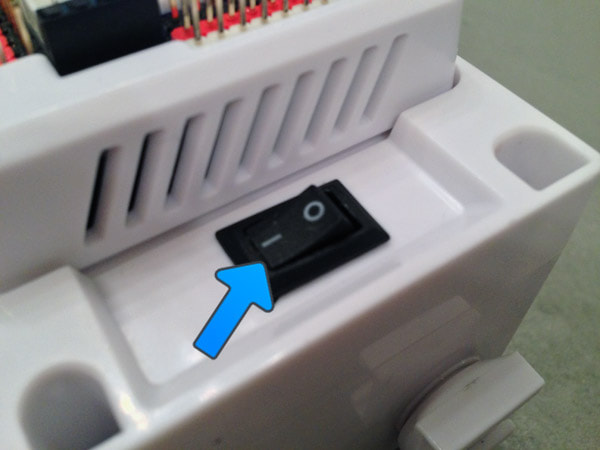
*Note: If you receive warning messages about missing EZ-Bits, then you should review the tutorial on Building the JD Robot before continuing. Step 5 Turn JD's power switch to the ON or "1" position. Early EZ-Robots have a power switch labelled OFF/ON, while the newer robots are labelled with a 0/1.
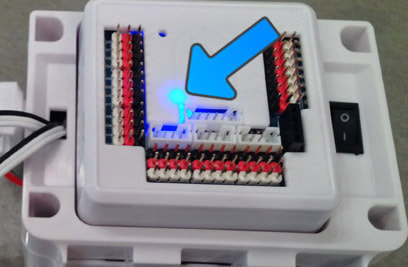
*Note: If you are running servos that do not have HDD on their label, they may be analog servos. Analog servos may jolt or twitch when the power is turned on. This is normal behavior. Step 6 When the power switch is turned to the ON position, the EZ-B will be flashing Blue. This means it is ready for a Wi-Fi connection.
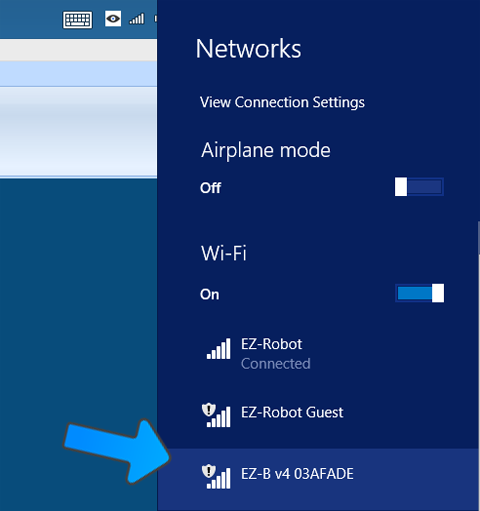
Here is a video of the expected startup sound, servo-motor twitch and RGB eyes lighting up when JD is powered on. Step 7 Locate JD's EZ-B Wi-Fi Access Point in your Wi-Fi Networks List. This is found by pressing the Wi-Fi button on your system tray in Windows. The EZ-B WiFi Access Point will always start with EZ-B v4 and can be renamed at a later point.
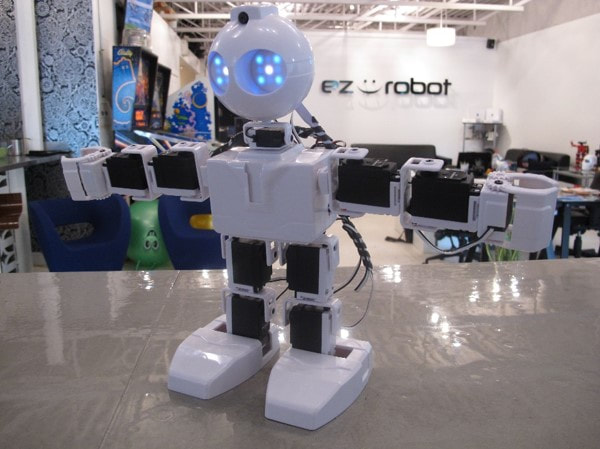
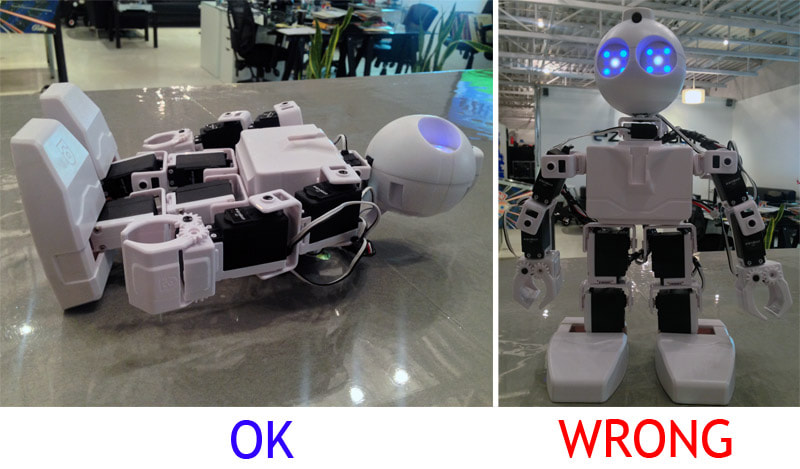
Step 8 Lay JD down on his back. Do not stand him up or he may fall when the connection occurs to the ARC software. When ARC connects to the robot, commands will automatically be sent that move JD's servos to their Calibration Position.
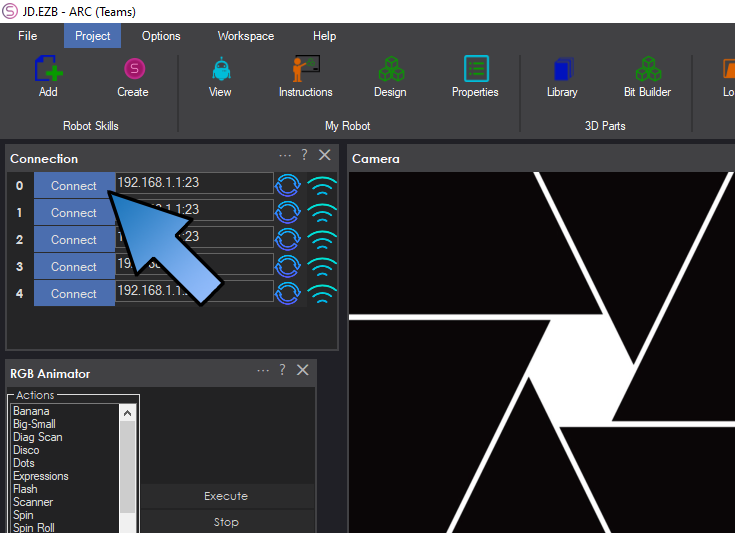
Step 9 Press the CONNECT button and a connection will occur from the PC to the EZ-B v4 in JD. His servos will instantly move into the calibration position.
*Note: If your EZ-Robot is older and has analog HD Servos, it is normal for the servos to make buzzing noises until your robot is calibrated. Once the servo motors are properly calibrated, they should remain silent when the robot is in standing position. EZ-Robot's more recent HDD servo motors will not make a noise while holding weight, but should still be calibrated to reduce load and heat, and to prolong servo life. Step 10 Once connected, JD will jump into the calibration position. The calibration position has JD's arms out and feet flat. Note that the bottom of the feet should be flat on the table or floor once the robot's ankle servos are properly aligned.
If the joints of JD do not initialize to the correct position, demonstrated in the above image, shut down the robot and skip to the Calibration Procedure in troubleshooting before operating JD. Complete Advance to the next lesson - we're close to having JD doing awesome stuff! |